
Wind instrument of the woodwind family
Sound production: the blown air is set into vibration by a bevel arranged at the mouthpiece.
Particularity: it owes its name to the horizontal position in which it is held when played
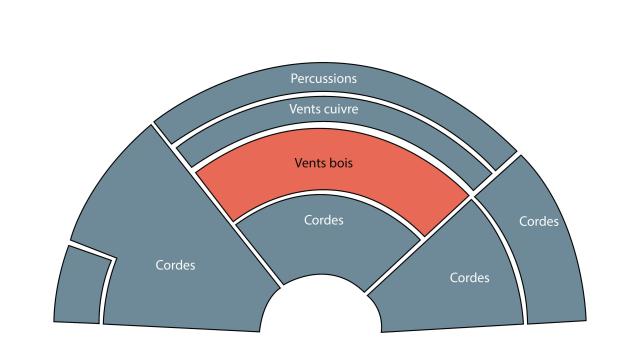
Place in the orchestra: wind/woodwind


![Mozart - Flute Concerto No.1 in G Major K.313 - I. Allegro maestoso [Flute Sheet Music]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi_webp/Jk_QciBEAQM/maxresdefault.webp)
